Twin Shaft Concrete Mixer Design
A twin shaft concrete mixer is a core device that efficiently mixes concrete materials (sand, gravel, cement, water, and admixtures) through the coordinated rotation of two parallel shafts. The twin shaft concrete mixer design focuses on the mixing drum, transmission mechanism, mixing mechanism, discharge device, and auxiliary systems. The counter-rotating twin shafts and spiral blades achieve efficient forced mixing.
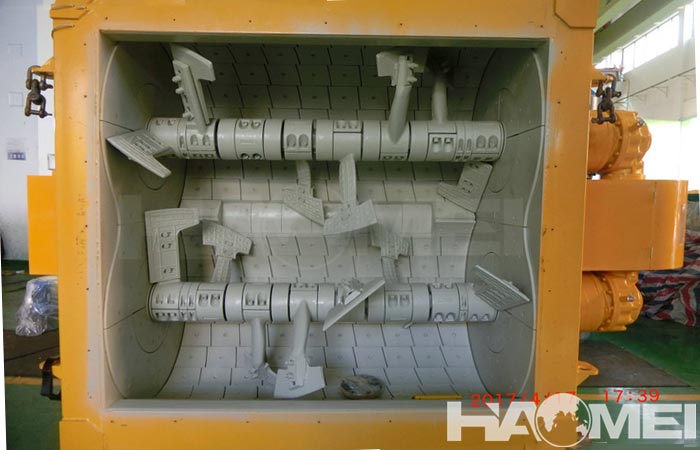
I. Core Structural Design
1. Mixing Drum
- Material and Structure:
Made of high-quality steel plates welded into a circular trough or twin-cylinder shape, this ensures sufficient rigidity and toughness to withstand the impact of hard aggregates.
- Functional Design:
The drum is equipped with an observation window, discharge door, safety switch, and feed port for easy operation and monitoring. A wear-resistant lining extends service life and reduces material residue.
2. Transmission Mechanism
- Drive Method:
Dual Motor Drive: The two mixing shafts are driven by independent motors, transmitted through a worm gear reducer (reduction ratio i=20) to ensure synchronized speeds.
Coupling: A roller chain coupling connects the two shafts to compensate for manufacturing precision and assembly errors and prevent speed variations.
- Optimized Layout:
The motor and reducer are mounted on top and connected via a self-tensioning belt, reducing noise, oil leakage, and preventing abnormal damage.
3. Mixing Mechanism
Dual-Shaft Counter-Rotation: Two horizontal mixing shafts are mounted in parallel and rotate in opposite directions, creating a three-dimensional motion path for thorough convection mixing of the material.
- Blade Design:
Spiral Arrangement: The blades are arranged in a spiral pattern along the axial direction, staggered front and back, up and down, to avoid dead zones.
Streamlined Agitator Arm: The mounting angle can be adjusted to 90° or 60° to optimize the mixing effect according to the concrete mixer's application.
Material and Thickness: 16Mn steel is used, with a blade thickness of 12mm and a barrel wall thickness of 10mm, ensuring wear resistance and strength.
Operating Principle: The blades use a forced mixing action, including shearing, squeezing, tumbling, and throwing, to uniformly mix the material during the intense relative motion.
II. Auxiliary System Design
1. Discharge Device
Bottom-Opening Discharge: Suitable for small and medium-capacity models (such as 500L), it quickly discharges concrete through the bottom discharge door, preventing the risk of rollover.
Integral, wide-opening discharge door: Minimizes residual volume and eliminates material accumulation, improving production efficiency.
2. Water System
Atomization Device: Utilizes an MP-type centrifugal pressure nozzle atomizer to atomize water into particles with a diameter of 100-500μm, thoroughly homogenizing it with the material.
Water Supply Control: Flow meters and valves precisely control the water addition rate to ensure a stable concrete moisture content (12%-14%).
3. Sealing and Lubrication
Shaft End Seals: Utilize a multi-seal structure (e.g., labyrinth seal + rubber seal) to prevent material leakage and bearing damage.
Lubrication System: A centralized lubrication system regularly supplies oil to bearings and gears, reducing wear.
III. Core Design Optimization Directions
- Wear Resistance Optimization:
The mixing drum lining and blades utilize "high-manganese steel with a welded wear-resistant layer," and the shaft end seal utilizes a multi-layer composite structure to extend the life of vulnerable parts.
- Mixing Efficiency Optimization:
Dual counter-rotating shafts and staggered spiral blades ensure seamless convection of materials, reducing mixing time to 30-40 seconds (for dry, hard concrete).
- Maintenance Ease Optimization:
The lining and blades are bolted (rather than welded) for quick and easy replacement. Access ports are provided for the reducer and bearing housing to reduce maintenance time.
- Safety Optimization:
Overload, overtemperature, and emergency stop protections are provided, and a guardrail is installed on the frame to prevent workplace accidents.
Through this structural design, the twin shaft concrete mixer can meet the mixing needs of various concrete types, including dry, hard, plastic, and fluid concrete, and is widely used in commercial concrete batching plants, precast component plants, and construction sites.

